Author Affiliations
Abstract
1 School of Physical Science and Technology, Xinjiang University, Urumqi 830046, China
2 School of Information Science and Engineering, Xinjiang University, Urumqi 830046, China
3 Key Laboratory of Signal Detection and Processing, Xinjiang Uygur Autonomous Region, Xinjiang University, Urumqi 830046, China
In order to solve this problem, a new biological detection method is proposed, which makes use of the characteristics of optical transmission at the edge of the spectral band gap and sensitive to refractive index variation. When the probe light with wavelength at the edge of the Bragg band gap of porous silicon is incident on the surface of porous silicon, the change of refractive index caused by deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) reaction in porous silicon will affect the detection light intensity transmitted from the porous silicon sensor. By analyzing the change of the average gray value of the transmitted light image, the concentration of the DNA can be obtained.
光电子快报(英文版)
2021, 17(9): 552
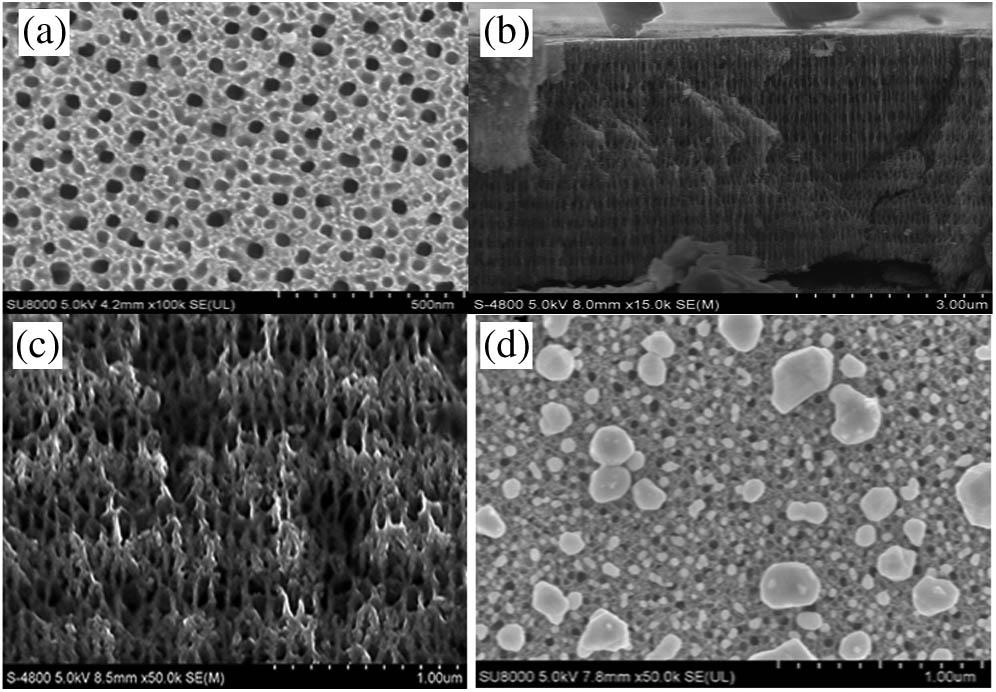
Author Affiliations
Abstract
1 School of Physical Science and Technology, Xinjiang University, Urumqi 830046, China
2 Affiliated Tumor Hospital of Xinjiang Medical University, Urumqi 830000, China
3 Department of Engineering, China University of Petroleum-Beijing, Keramayi 834000, China
4 School of Information Science and Engineering, Xinjiang University, Urumqi 830046, China
5 School of Electronic Engineering, Beijing University of Posts and Telecommunications, Beijing 100876, China
6 Quality of Products Supervision and Inspection Institute, Urumqi 830011, China
In this Letter, the surface-enhanced Raman scattering (SERS) signal of early breast cancer (BRC) patient serum is obtained by a composite silver nanoparticles (Ag NPs) PSi Bragg reflector SERS substrate. Based on these advantages, the serum SERS signals of 30 normal people and 30 early BRC patients were detected by this substrate. After a baseline correction of the experimental data, principal component analysis and linear discriminant analysis were used to complete the data processing. The results showed that the diagnostic accuracy, specificity, and sensitivity of the composite Ag NPs PSi Bragg reflector SERS substrate were 95%, 96.7%, and 93.3%, respectively. The results of this exploratory study prove that the detection of early BRC serum based on a composite Ag NPs PSi Bragg reflector SERS substrate is with a stable strong SERS signal, and an unmarked and noninvasive BRC diagnosis technology. In the future, this technology can serve as a noninvasive clinical tool to detect cancer diseases and have a considerable impact on clinical medical detection.
porous silicon Bragg reflector surface-enhanced Raman scattering breast cancer detection principal component analysis linear discriminant analysis Chinese Optics Letters
2020, 18(5): 051701

Author Affiliations
Abstract
1 College of Chemistry and Chemical Engineering, Xinjiang University, Urumqi 830046, China
2 College of Information Science and Engineering, Xinjiang University, Urumqi 830046, China
3 College of Physical Science and Technology, Xinjiang University, Urumqi 830046, China
We present a technique for fabricating a fluorescence enhancement device composed of metal nanoparticles (NPs) and porous silicon (PSi) diffraction grating. The fluorescence emission enhancement properties of the PSi and the fluorescence enhancement of the probe molecules are studied on PSi gratings. The fluorescence enhancement of the probe molecules on a fluorescence enhancement device is further improved through the deposition of metal NPs onto the PSi grating. In comparison to metal NP/PSi devices, metal NP periodic distributions can produce a stronger fluorescence enhancement that couples with the PSi grating fluorescence enhancement to achieve an overall three-fold enhancement of the fluorescence intensity.
050.0050 Diffraction and gratings 230.0230 Optical devices Chinese Optics Letters
2017, 15(11): 110501
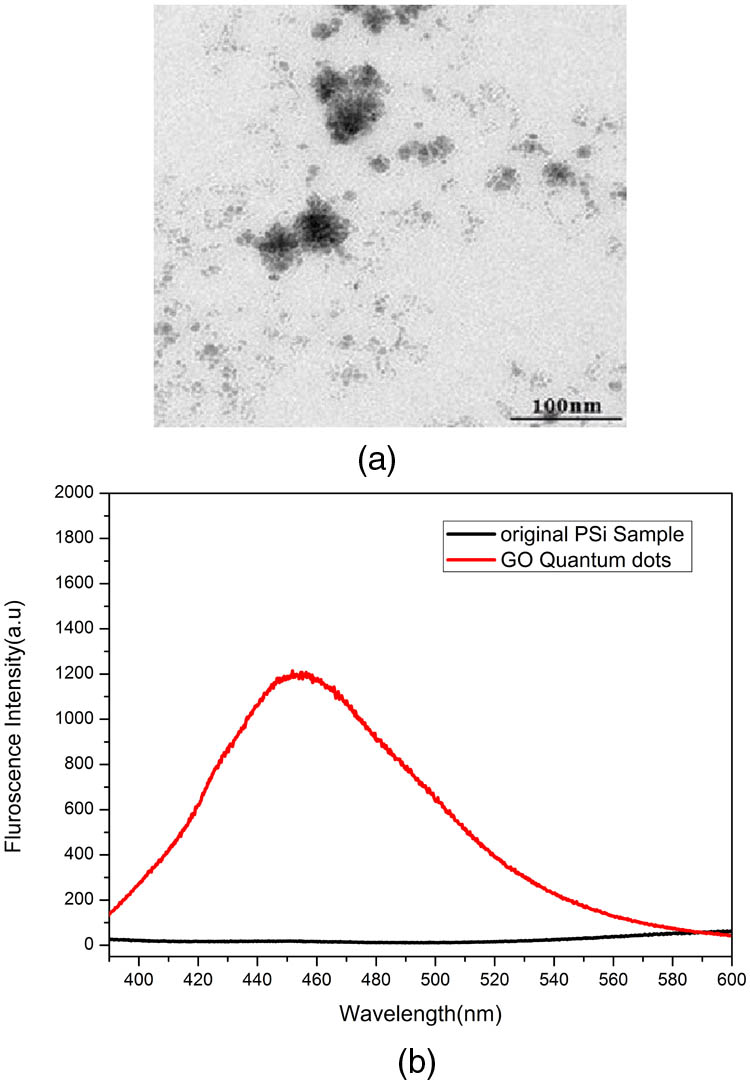
Author Affiliations
Abstract
1 School of Physical Science and Technology, Xinjiang University, Urumqi 830046, China
2 School of Information Science and Engineering, Xinjiang University, Urumqi 830046, China
3 Department of Physics, Ningbo University, Ningbo 315211, China
The fluorescence of graphene oxide quantum dots (GOQDs) that are infiltrated into porous silicon (PSi) is investigated. By dropping activated GOQDs solution onto silanized PSi samples, GOQDs are successfully infiltrated into a PSi device. The results indicate that the intensity of the fluorescence of the GOQD-infiltrated multilayer with a high reflection band located at its fluorescence spectra scope is approximately double that of the single layer sample. This indicates that the multilayer GOQD-infiltrated PSi substrate is a suitable material for the preparation of sensitive photoluminescence biosensors.
050.5298 Photonic crystals 120.5700 Reflection 130.3990 Micro-optical devices 160.2540 Fluorescent and luminescent materials 160.4760 Optical properties Chinese Optics Letters
2016, 14(4): 041601
Author Affiliations
Abstract
A porous silicon microcavity (PSM) is highly sensitive for sensing applications due to its high surface area and a narrow resonance peak. In this letter, we fabricated the PSM by alternate current density from a low value to a high value during double-tank electrochemical anodization at different electrolyte temperatures. Results show that with the increase of the electrolyte temperature, the rate of the PS etching becomes faster and the refractive index of the PS layer becomes smaller. The thickness of the PS increases faster than the decrease of the refractive index of the PS.
240.6695 Surface-enhanced Raman scattering 160.4670 Optical materials 160.3900 Metals 300.6450 Spectroscopy, Raman Chinese Optics Letters
2014, 12(s1): S12402
1 石河子大学 信息科学与技术学院,新疆 石河子 832003
2 新疆大学 信息科学与工程学院,乌鲁木齐 830046
采用双槽电化学腐蚀法制备了纳米多孔硅,主要研究了腐蚀时间和腐蚀电流对重掺杂p型(100)硅衬底上制备的多孔硅层有效光学厚度的影响,采用U4100光谱仪、场发射扫描电子显微镜(FESEM)技术对所制备的多孔硅光子晶体的结构和有效光学厚度进行了分析表征。研究结果表明,通过合理地选择腐蚀时间和腐蚀电流,可以比较精确地制备特定有效光学厚度的多孔硅薄膜,此方法可广泛应用于纳米多孔硅光子晶体的制备中。
纳米硅 双槽电化学腐蚀 腐蚀条件 有效光学厚度 porous silicon doubletank electrochemical corrosion method etching conditions effective optical thickness
Author Affiliations
Abstract
1 School of Physics, Xinjiang University, Urumqi 830046, China
2 School of Electronic and Information Engineering, Xi'an Jiaotong University, Xi'an 710049, China
3 Key Laboratory of Xinjiang Biological Resources and Gene Engineering, College of Life Sciences and Technology, Xinjiang University, Urumqi 830046, China
4 College of Information Science and Engineering, Xinjiang University, Urumqi 830046, China
Porous silicon (PS) suitable for optical detection of immunoreaction is fabricated. The structure of immunosensor is prepared by the following steps: oxidization, silanization, glutaraldehyde cross-linker, and covalent binding of antibody. When antigen is added into the immunosensor, the Raman intensity is estimated to be linearly reduced according to the concentration of the surface protective antigen protein A (spaA) of below 4.0 μg·ml?1. The ultimate detection limit is 1.412×10^2 pg.ml^{?1}. Controlled experiments are also presented with non-immune antigen of the spaA, and results show that the immunosensor has high specificity. Compared with the conventional enzyme-linked immuno sorbent assay (ELISA), this method is quick, inexpensive, and label-free.
多孔硅 免疫传感器 猪丹毒丝菌表面保护性抗原A 拉曼光谱 光学检测 280.1415 Biological sensing and sensors 070.0070 Fourier optics and signal processing 070.4790 Spectrum analysis 280.0280 Remote sensing and sensors Chinese Optics Letters
2011, 9(2): 022801
Author Affiliations
Abstract
1 School of Electronic and Information Engineering, Xi'an Jiaotong University, Xi'an 710049, China
2 School of Materials Science and Engineering, Tongji University, Shanghai 200092, China
3 School of Chemistry and Chemical Engineering, Xinjiang University, Urumqi 830046, China
4 College of Information Science and Engineering, Xinjiang University, Urumqi 830046, China
A TiO2/porous silicon (PS) composite system is prepared by chemical vapor deposition. The crystal form with anatase phase of the samples is evaluated by X-ray diffraction and ultraviolet-visible (UV-vis) absorbance spectra, and the morphology with microsphere of TiO2 particles is characterized by scanning electron microscopy. The composite system formed by this technique gives a broad blue luminescence and the mechanism of photoluminescence with TiO2/PS is also discussed.
多孔硅 二氧化钛(TiO2) 复合体系 光致发光 160.4670 Optical materials 310.6860 Thin films, optical properties 240.0310 Thin films 250.5230 Photoluminescence Chinese Optics Letters
2010, 8(6): 618
新疆大学信息科学与工程学院,乌鲁木齐 830046
用Bruggeman模型理论,分析了氧化多孔硅/聚合物复合膜的等效折射率与多孔硅孔隙率、氧化度和嵌入率的关系.实验研究了嵌入PMMA材料的氧化多孔硅/聚合物膜的等效折射率.证实了在多孔硅中嵌入聚合物可使薄膜的光学参量保持稳定.
氧化多孔硅 聚合物 复合膜 折射率 Oxidized porous silicon Polymer Composite film Refractive index
Author Affiliations
Abstract
1 College of Information Science &
2 Engineering, Xinjiang University, Urumqi 830046
The equation for calculating the effective refractive index of porous silicon inserted polymer was obtained by three-component Bruggeman effective medium model. The dependence of the effective refractive index of porous silicon/polymer composite films on the polymer fraction with various initial porosity was given theorically and experimentally respectively. The porous silicon and polymer polymethylmetacrylate based dispersive red one (PMMA/DR1) composite films were fabricated in our experiments. It is found that the measured effective refractive index of porous silicon inserted polymer was slightly lower than the calculated result because of the oxidization of porous silicon. The effective refractive index of oxidized porous silicon inserted polymer also was analyzed by four-component medium system.
240.0310 thin films 160.4670 optical materials 160.5470 polymers Chinese Optics Letters
2005, 3(10): 10608





